
However, a “black-box pragmatic study“ 17 to validate the accuracy of bloodless detection of dyskalemias based on AI-ECG is still warranted before integration into routine clinical workflows. Based on analysis of an annotated 66,000-ECG dataset, we have successfully used DLM to develop ECG12Net for the rapid quantitative estimation of blood K + concentration to detect dyskalemias in the ED 6. With the revolution and advancement of artificial intelligence (AI) techniques, deep learning models (DLM) 9 have been shown to achieve human-level performance and effectively detect cardiac diseases with large annotated ECG datasets 10, 11, 12, 13, 14, 15, 16. However, these morphologic ECG changes associated with dyskalemias may not be easily recognized even by experienced physicians or cardiologists. Traditionally, the diagnosis of dyskalemia relies on blood tests with varying turnaround times 7.Įlectrocardiography (ECG), as a prompt, non-invasive, and convenient bedside tool, may detect electrical changes associated with dyskalemias, including altered PR interval, QRS, ST-segment, T-wave amplitude, and/or corrected QT interval 8. In our recent study, 22% and 2% of all patients visiting the emergency department (ED) had hypokalemia and hyperkalemia, respectively 6.
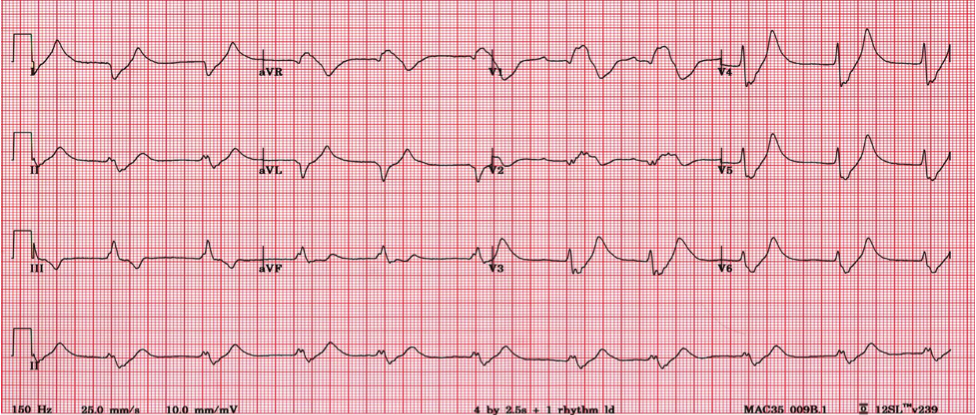
Up to 20–50% of patients hospitalized for acute illnesses have hypokalemia (plasma K + value ≤3.5 mmol/L) and 2–5% have hyperkalemia (K + ≥5.5 mmol/L) 5. Dyskalemia causes cardiovascular, neuromuscular, renal and metabolic disturbances, and is a common electrolyte abnormality associated with cardiovascular complications and increased mortality 3, 4. Thus, dyskalemias, including hypokalemia and hyperkalemia, usually arises from derangements of transcellular K + shift 1 and/or defective renal/extrarenal K + excretion 2. The concentration of K + in plasma is determined by the distribution of K + between intracellular and extracellular fluid (ECF) and by renal K + excretion. Potassium (K +) is the principal intracellular cation and functions to maintain the electrical gradient across cell membranes. Point-of-care bloodless AI ECG-K + not only rapidly identified potentially severe hypo- and hyperkalemia, but also may serve as a biomarker for medical complexity and an independent predictor for adverse outcomes. In addition, patients with normal Lab-K + but dyskalemic ECG-K + (pseudo-positive) also exhibited more co-morbidities and had worse outcomes.
#Hyperkalemia ecg findings full#
Compared to hypokalemic Lab-K +, patients with hypokalemic ECG-K + had significantly higher risk for adverse outcomes after full confounder adjustment. ECG-K + and Lab-K + hyperkalemia were associated with high HRs for 30-day all-cause mortality. The U-shaped relationships between K + concentration and adverse outcomes were more prominent for ECG-K + than for Lab-K +. Area under receiver operating characteristic curves for ECG-K + to predict moderate-to-severe hypokalemia (Lab-K + ≤3 mmol/L) and moderate-to-severe hyperkalemia (Lab-K + ≥ 6 mmol/L) were >0.85 and >0.95, respectively. ECG-K + had mean absolute errors (MAEs) of ≤0.365 mmol/L. In total, 26,499 patients with 34,803 emergency department (ED) visits to an academic medical center and 6492 ED visits from 4747 patients to a community hospital who had a 12-lead ECG to estimate ECG-K + and serum laboratory potassium measurement (Lab-K +) within 1 h were included.

This retrospective cohort study was done at two hospitals within a health system from May 2019 to December 2020. The aims of this study were to determine the clinical accuracy of AI-assisted ECG for dyskalemia and prognostic ability on clinical outcomes such as all-cause mortality, hospitalizations, and ED revisits. Artificial intelligence (AI)-assisted electrocardiography (ECG) has been evaluated as an early-detection approach for dyskalemia. Dyskalemias are common electrolyte disorders associated with high cardiovascular risk.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
